Think of navigating international shipping as conquering a spicy Thai dish - you're not sure how it's gonna go, but you're excited for the adventure! The often complex landscape of freight shipping, understanding rates, transit times, and customs regulations between Thailand and South Korea can seem daunting. This destination guide aims to lay out the process in a digestible manner, shedding light on various freight options including air, sea, road, and rail. It will delve into the intricacies of customs clearance, duties, and taxes, delivering practical advice for businesses. If the process still feels overwhelming, let DocShipper handle it for you! As an experienced international freight forwarder, we transform these challenges into seamless experiences and prosperous ventures for your business.
Table of Contents
Which are the different modes of transportation between Thailand and South Korea?
When shipping goods between Thailand and South Korea, it's like deciding on the best route for a marathon – every decision matters for the smooth run. Both countries are neighbors in the same region, with the sea as their playground and air as their sky bridge. However, with no land connectivity, those methods become the star players on the field. Understanding these geographical constraints, it's essential to choose either ocean or air shipping wisely, aligning with your business' unique needs. Imagine it as choosing between a powerful elephant (seafaring) or a swift falcon (airfreight), each with its own pros and cons. The game, therefore, is in the choosing.
How can Siam Shipping help?
Shipping goods between Thailand and South Korea? Let DocShipper simplify the process for you. Our experts organize every aspect, from transportation arrangements to customs clearance. Have a question? Ask our consultants! It's free. Need an estimate? Get one within 24 hours. Reach out to DocShipper now and let us make international shipping effortless for you.
Siam Shipping Tip: Consider ocean freight if:
- You are shipping large volumes or bulky items, as sea freight offers the most space at a cost-effective rate.
- You're not racing against the clock. Ocean freight takes its sweet time, especially when stacked up against other transport methods.
- Your supply chain is linked up with big-name ports. Think of it as the VIP lane on the maritime superhighway.
Sea freight between Thailand and South Korea
Welcome to the comprehensive guide for transporting goods via ocean between Thailand and South Korea – two vibrant nations intertwined in a dynamic trading liaison. Thailand's bustling port of Laem Chabang goes hand-in-glove with South Korea's Busan Port, forming a maritime lifeline for the myriad of goods exchanged, from electronics to automotive parts. Opting for sea freight may test your patience, but it sure rewards your wallet, especially when handling bulk shipments.
However, let's dive beneath the surface. The reality isn't as smooth as our oceanic analogy! Lots of shippers find themselves tangled in a logistical labyrinth, grappling with regulatory nuances and operational pitfalls. Are you one of them? Clueless about how to navigate this trade route without stumbling into common missteps? Stay tuned. We'll unravel the knots for you, piece by piece, showcasing the best practices and specifications required. We're about to turn what feels like decoding a cryptic maritime Morse code into a smooth sailing journey. Prepare for insightful revelations that can make your maritime endeavor between Thailand and South Korea just a breeze!
Main shipping ports in Thailand
Laem Chabang Port
Location and Volume: Located just north of Pattaya, this port is the most significant in Thailand, with a shipping volume of over 8 million TEU per year. Known for its deep-water and large-capacity facilities, it plays a crucial role in the region's trade.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Laem Chabang's primary trading partners include China, Japan, and the USA. Its strategic location near Bangkok and accessibility via road and rail links contribute to its importance for ASEAN trade.
Context for Businesses: If your business is looking to establish or expand in the East Asian market, the Laem Chabang Port can facilitate access to some of the fastest-growing economies in the region. It's well-equipped to handle high shipping volumes, making it great for businesses with considerable shipping needs.
Bangkok Port
Location and Volume: Located in Khlong Toei and the city of Bangkok, this port is the second busiest in Thailand and handles over 1 million TEU of cargo annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Apart from its neighbouring countries, the Bangkok Port swaps significant amounts of cargo with China, Asia Pacific countries, and the United States. Its proximity to the heart of Thailand's capital city makes it an indispensable asset for businesses operating within and beyond ASEAN boundaries.
Context for Businesses: For those companies planning to penetrate the bustling markets of Bangkok and capitalize on the vibrant South East Asian economies, Bangkok Port stands as an advantageous choice, given its urban centrality and the ease of further distribution via Thailand's vast intercity transport network.
Songkhla Port
Location and Volume: Located on the southern gulf coast of Thailand, Songkhla Port plays a secondary role in the country's shipping, managing over 100,000 TEU annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Songkhla Port has significant trade linkages with neighbouring Malaysia and Indonesia, as well as countries afar like Australia and China. The port specializes in handling natural resources like coal, timber, and rubber.
Context for Businesses: If your business entails trading natural resources, leveraging the Songkhla Port could be strategically advantageous. Apart from its relevant dealing in natural resources, you might consider the port advantageous for shipping to and from the South of Thailand and neighbouring countries.
Map Ta Phut Port
Location and Volume: Settled on the eastern seaboard, Map Ta Phut Port is one of Thailand's prime ports dealing with massive industrial shipments, handling around 900,000 TEU each year.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: The port is a vital commerce node with partners including China, Japan, and Singapore. It serves as a crucial driver within Thailand's Eastern Economic Corridor initiative.
Context for Businesses: Map Ta Phut Port might serve as your springboard into Thailand's burgeoning industrial sector. With its specialized role in shipping industrial goods and chemicals, Map Ta Phut could propel your business success in these sectors.
Sattahip Commercial Port
Location and Volume: Located in the eastern region of Thailand, the Sattahip Commercial Port may be smaller in scale, but it plays a significant role in the nation's import/export activities, dealing with over 50,000 TEU annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Most of its commercial relationships exist with countries in the ASEAN region, China, and the United States. It hosts a notable naval base, contributing to its strategic importance.
Context for Businesses: If your business strategy centers around the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region, Sattahip Commercial Port can be a smart choice. It's well-positioned to serve businesses seeking strong ASEAN market connections.
Phuket Deep Sea Port
Location and Volume: Located on the Andaman Sea, Phuket Port is smaller in scale, handling approximately 100,000 TEU annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: This port primarily services the tourist industry and trades significantly with nearby countries, including Malaysia and Indonesia.
Context for Businesses: Businesses in the tourism or luxury sector could see the benefits of leveraging Phuket Deep Sea Port. The port's capacity to handle cruise ships alongside regular cargo makes it a unique option for those looking to tap into Thailand's thriving tourism market.
Main shipping ports in South Korea
Busan Port
Location and Volume: Situated on the southeastern tip of the Korean Peninsula, Busan Port plays a pivotal role in trade across Northeast Asia. It boasts a staggering shipping volume of over 20 million TEU.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: It serves as the main port for trading with key partners including China, Japan, the US, and Singapore. The port provides strategic access to major global shipping routes.
Context for Businesses: If your business aims to penetrate the Northeast Asian markets, Busan Port, with its advanced infrastructure and frequent shipping routes, could be a critical element in your strategy.
Incheon Port
Location and Volume: Positioned on the northwestern coast of South Korea, Incheon Port handles over 3 million TEU, the second largest volume in the country.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Traders primarily from China, Japan, Vietnam, and the US utilize the port. It has profound strategic importance due to its proximity to capital city Seoul.
Context for Businesses: With its modernized container terminals and extensive hinterland in Seoul metropolitan area, Incheon Port can provide efficient distribution channels if you aim to target South Korean local markets.
Pyongtaek-Dangjin Port
Location and Volume: Located on the western coast of South Korea, Pyongtaek-Dangjin Port handles about 1.7 million TEU annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Its key trading partners include China, Japan, and Southeast Asian countries with significance as a major import/export point for automobiles.
Context for Businesses: If your operations involve automobile or auto-parts transport, Pyongtaek-Dangjin Port's specialized facilities could significantly streamline your logistics process.
Gwangyang Port
Location and Volume: Positioned on the southern coast of South Korea, Gwangyang Port manages a volume of more than 2 million TEU annually.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: It has strong trade connections mainly with China, ASEAN countries, and the US. Its strategic importance lies in its role as the hub of petrochemical and steel industries.
Context for Businesses: If you're in the petrochemical or steel industry, leveraging Gwangyang Port's specialty cargo handling capabilities may improve your supply chain efficiency.
Mokpo Port
Location and Volume: Situated on the southwestern coast of South Korea, Mokpo Port is relatively smaller with shipping volume of around 14,000 TEU.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: Key trading partners include China, Japan, and Vietnam. It has a unique importance in connecting Korea’s southwestern islands.
Context for Businesses: Businesses focusing on regional trade and exploiting lesser crowded ports might find Mokpo Port beneficial due to its strategic location and less congestion.
Ulsan Port
Location and Volume: Positioned on the east coast of South Korea, Ulsan Port currently handles over 430,000 TEU per year.
Key Trading Partners and Strategic Importance: China, Japan, and the US are the top trading partners. Its proximity to Ulsan Industrial Complex offers key strategic advantages.
Context for Businesses: If you’re involved in the heavy industry, Ulsan Port's close connection to a major manufacturing hub could significantly aid your logistics strategy. Its specialization in petroleum and chemical shipment also offers distinct advantages.
Should I choose FCL or LCL when shipping between Thailand and South Korea?
When shipping goods from Thailand to South Korea, choosing between Full Container Load (FCL) or Less than Container Load (LCL), also known as consolidation, is a strategic decision. This choice directly impacts your cargo's cost, delivery time, and overall shipping success. Let's dive into understanding the differences to make an informed decision, considering your specific shipping needs. Remember, getting it right could mean the difference between smoother operations or unexpected hiccups. Let's set sail on this sea of knowledge!
LCL: Less than Container Load
Definition: LCL (Less than Container Load) shipping is a method where your goods share container space with others. It's a cost-effective option when you don't have enough cargo to fill an entire container.
When to Use: Opt for LCL shipment when your cargo volume is less than 13/14/15 CBM. This makes it flexible for low volumes, letting you pay only for the space your cargo occupies in the shared container.
Example: Consider a sporting goods store in Bangkok with orders to ship 10 CBM of soccer balls to a store in Seoul. Since the volume is less than a full container load, an LCL freight is an appropriate choice to conserve cost and space.
Cost Implications: While per unit pricing may be higher in LCL compared to FCL (Full Container Load), it's beneficial for less than full-load cases. You would only pay for the space you use, which can lead to substantial savings if your shipment doesn't require a full container. Always consider the volume, weight, and nature of your goods when considering LCL shipping quotes.
FCL: Full Container Load
Definition: FCL (Full Container Load) shipping is when a single entity reserves an entire container for transporting goods, usually in either a 20'ft or 40'ft container.
When to Use: FCL becomes the more economical and secure option when the cargo exceeds 13/14/15 CBM. Because the FCL container is sealed from origin to destination, it adds an extra layer of security - you're mitigating the risk of damage from shared cargo.
Example: Consider a Thai automotive parts manufacturer exporting various parts equal to 17 CBM to a client in South Korea. It would be more cost-effective and safe for them to secure a 20'ft FCL container for their shipment.
Cost Implications: While FCL shipping quotes may seem higher than LCL (Less than Container Load), keep in mind that the cost per unit is often lower, especially for higher-volume shipments. Also, potential risks associated with cargo sharing are decreased, which can indirectly save you from unforeseen expenses. Be sure to compare prices and factor in all variables before making a choice.
Unlock hassle-free shipping
Are you puzzled over whether to ship by consolidation or full container from Thailand to South Korea? Let DocShipper help! With our mission to make cargo shipping hassle-free, our ocean freight experts assist in determining the optimal choice based on payload size, budget, and delivery timeline. We create personalized, seamless shipping scenarios tailored to your needs. Ready to take your business global without the worry? Reach out for a free shipping estimation now!
How long does sea freight take between Thailand and South Korea?
Sea freights between Thailand and South Korea typically average around twenty days. However, keep in mind that transit times are influenced by factors such as the specific port of departure and arrival, the weight and nature of goods, and certain seasonal considerations. To get the most accurate estimation, turn to a freight forwarder like DocShipper that can provide a tailored quote for your shipping needs.
Here's a simple comparison chart displaying the average transit times in days for sea freight between the main ports in Thailand and South Korea:
| Port in Thailand | Port in South Korea | Average Transit Time |
| Port of Laem Chabang | Port of Busan | 22 |
| Port of Bangkok | Port of Incheon | 25 |
| Map Ta Phut | Port of Gwangyang | 26 |
| Port of Songkhla | Port of Ulsan | 24 |
Please note, these figures can fluctuate, so it's always best to get a bespoke quote for your specific freight needs.
How much does it cost to ship a container between Thailand and South Korea?
Ocean freight rates for shipping a container between Thailand and South Korea can range widely. Due to factors such as the point of loading and destination, carrier choice, goods' nature, and monthly market fluctuations, a specific shipping cost can't be offered upfront. We understand this ambiguity might be overwhelming. But worry not, our shipping specialists take these factors into account, and they strive to offer the best possible rates tailored to your unique needs, ensuring you get value for every cent. Rest assured, we quote on a case-by-case basis, optimizing your cost scenario without any compromise on service quality. Be sure to consult us for your specific shipping requirements.
Special transportation services
Out of Gauge (OOG) Container
Definition: Out of Gauge (OOG) containers are special containers used for cargos that don't fit within the dimensions of a standard container, hence the term 'out of gauge cargo'. These containers have flat racks that can hold wide or long goods.
Suitable for: OOG containers are ideal for transporting large items, such as heavy machinery and industrial equipment, artworks and architectural structures.
Examples: For example, a business shipping turbine parts, tractors, or construction equipment from Thailand to South Korea would benefit from using an OOG container.
Why it might be the best choice for you: If your cargo doesn't fit into the dimensions of a standard shipping container, an OOG container can handle those odd sizes and shapes, avoiding potential damage during the journey.
Break Bulk
Definition: Break bulk refers to goods that must be loaded individually and not in containerized cargo, or in other words, loose cargo load.
Suitable for: Break bulk is suitable for the shipment of goods that are oversized, heavy, or on pallets, such as construction equipment, massive vehicle parts, iron, or wood beams.
Examples: If your business involves shipping giant propellers or substantial crates of heavy machinery from Thailand to South Korea, break bulk could be the best choice.
Why it might be the best choice for you: Break bulk allows for the individual handling of each item, which means that each piece can be given the special attention it requires.
Dry Bulk
Definition: Dry bulk usually refers to granular products shipped in large quantities, such as grain, coal, and minerals.
Suitable for: Dry bulk is ideal for large volumes of homogenous products like gravel, sand, or cereals.
Examples: An agricultural business exporting large quantities of rice, or a mining company shipping iron ore from Thailand to South Korea could benefit from dry bulk shipping.
Why it might be the best choice for you: Dry bulk shipping is cost-effective for transporting vast quantities of granular products, reducing your overall expenditure on shipping.
Roll-on/Roll-off (Ro-Ro)
Definition: Roll-on/Roll-off (Ro-Ro) service refers to a type of vessel equipped to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, trailers, and railroad cars that are driven on and off the ro-ro vessel on their own wheels.
Suitable for: Ro-Ro is suitable for all self-propelled cargos, these are typically vehicles.
Examples: If you're involved in exporting cars, trucks, or heavy equipment like cranes from Thailand to South Korea, Ro-Ro service is your ideal choice.
Why it might be the best choice for you: Ro-Ro helps ensure your vehicles arrive in the same condition as when they were shipped, due to the minimal handling of the cargo.
Reefer Containers
Definition: Reefer containers are essentially refrigerated containers used to ship perishable goods that must be maintained at a constant temperature.
Suitable for: Reefer containers are suitable for fresh produce, seafood, dairy products, or any perishable goods.
Examples: They are ideal for businesses in Thailand shipping seafood, tropical fruits, or dairy products to South Korea.
Why it might be the best choice for you: Using reefer containers ensures your perishable goods reach their destination fresh and ready for consumption, maximizing their value upon arrival.
For more insights into your shipping needs between Thailand and South Korea, DocShipper can help you make the right choice based on your specific requirements. We invite you to contact us for a free shipping quote in less than 24 hours. Make the right move with DocShipper for your shipping solutions.
Siam Shipping Tip: Consider Air freight if:
- Time's ticking and you can't wait. Air freight is like the express train of shipping; it's the quickest way to get your stuff from A to B.
- You're not shipping a warehouse. If your cargo is under 2 CBM, air freight is a snug fit for your smaller haul.
- Your supply chain ends somewhere off the beaten path. Airports are everywhere, so you can get your goods to those hard-to-reach spots.
Air freight between Thailand and South Korea
Speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make air freight the star player for shipping from Thailand to South Korea, especially for small, high-value items. Imagine you're shipping a compact batch of artisanal silk scarves, or perhaps cutting-edge electronic components. Almost like an express elevator, air freight whisks these goods away faster than any other shipping method, also assuring consistent delivery times.
However, shippers often trip over unseen obstacles by overlooking crucial factors in air freight. It's like ordering a fancy dish without knowing its ingredients: you might end up paying more than you bargained for! Incorrectly estimating the shipping cost by miscalculating the weight of goods, or being unaware of the best practices, can turn what could have been a cost-effective shipment into an expensive error. These common missteps underscore the importance of getting your ducks in a row for successful air freight experience. In the following guide, we'll dive into details, illuminating these often-overlooked factors on your path to ace air freight between Thailand and South Korea.
Air Cargo vs Express Air Freight: How should I ship?
Struggling to choose the right shipping method for your precious cargo from the Land of Smiles, Thailand, to the Land of Morning Calm, South Korea? Let's clear this up casually: think of air cargo as hitching a ride in a friendly-neighbor's plane, while express air freight is like having your own private jet, dedicated and swift. In the upcoming discussion, we'll untangle the details, helping you make the best call for your business.
Should I choose Air Cargo between Thailand and South Korea?
Considering air cargo for shipping goods between Thailand and South Korea? This choice can be highly cost-effective and reliable. For example, airlines like Korean Air and Thai Airways play a crucial role in international freight. However, be mindful of the longer transit times due to their fixed schedules. If your consignment exceeds 100/150 kg (220/330 lbs), air cargo becomes increasingly cost-efficient. Make sure to evaluate your budget and shipping needs carefully when choosing this mode of transport.
Should I choose Express Air Freight between Thailand and South Korea?
Express air freight, a service specializing in the transport of goods using cargo-only aircraft, can be a swift and efficient shipping solution between Thailand and South Korea, particularly for shipments below 1 CBM or 100/150 kg (220/330 lbs). Firms like FedEx, UPS or DHL can offer reliable express shipping, ensuring your cargo reaches its destination promptly. If your business frequently deals with time-critical or smaller shipments, choosing express air freight could significantly streamline your logistics and enhance customer satisfaction.
Main international airports in Thailand
Suvarnabhumi Airport
Cargo Volume:
Suvarnabhumi Airport, one of the busiest cargo airports in Asia, handles over 1.5 million metric tons of cargo annually.
Key Trading Partners:
The airport primarily serves as a hub for cargo trading with China, Japan, the US, and several ASEAN countries, mainly Singapore and Malaysia.
Strategic Importance:
Located just outside of Bangkok, Suvarnabhumi Airport is strategically positioned for both domestic and international cargo movement. It is well connected with air, rail, and road networks, making it an essential gateway for international trade.
Notable Features:
The airport has advanced cargo handling facilities that allow for efficient processing of goods. Its air cargo area spans over 570,000 sq.m., comprising cargo terminals and a Free Zone.
For Your Business:
If speed and efficiency are a preference for your business, Suvarnabhumi's advanced and high-capacity handling facilities may streamline your shipping process, ensuring that your goods reach their destinations promptly.
Don Mueang International Airport
Cargo Volume:
While more recognized for passenger services, Don Mueang also handles 130,000 metric tons of cargo annually.
Key Trading Partners:
The key markets served by this airport are China, Japan, India, and other ASEAN countries, particularly Laos and Cambodia.
Strategic Importance:
Positioned in the heart of Bangkok, Don Mueang provides quick domestic connections and efficient access to the city's business districts, benefiting businesses with local logistics and distribution needs.
Notable Features:
The airport is home to several cargo airlines and freight companies, providing businesses with a variety of service options.
For Your Business:
If you have domestic distribution needs, or if your supply chain emphasizes the ASEAN region, the central location and efficient connections of Don Mueang might be a strategic fit for you.
Chiang Mai International Airport
Cargo Volume:
The airport handles about 16,000 metric tons of cargo annually.
Key Trading Partners:
The major partners include China, Singapore, and other ASEAN countries. It's also a significant hub for cargo flights to local destinations within Thailand.
Strategic Importance:
As the main international gateway to Northern Thailand, it's a strategic location for businesses in industries like tourism, agriculture, and handicrafts.
Notable Features:
The airport has a dedicated Cargo Terminal providing 24-hour service and an apron area capable of handling three B747 cargo aircraft simultaneously.
For Your Business:
If your business is centered around Northern Thailand's key industries, Chiang Mai Airport's location and facilities offer the accessibility and capacity to help streamline your cargo transport needs.
Main international airports in South Korea
Incheon International Airport
Cargo Volume: With a cargo volume of 2.75 million tons in 2020, it's one of the busiest cargo airports globally.
Key Trading Partners: Main trading partners include China, the USA, Vietnam, Japan, and Hong Kong, making this airport ideal for trans-continental trade.
Strategic Importance: Incheon Airport's strategic location serves as a hub for trans-Pacific and intra-Asian shipments.
Notable Features: The airport offers around-the-clock customs clearance, enabling efficient and uninterrupted cargo operations. It also hosts various cargo carriers, providing a range of shipping options.
For Your Business: If your business involves high-volume, intercontinental shipping, consider Incheon's significant cargo capabilities and its extensive connections to key global markets.
Gimpo International Airport
Cargo Volume: Handled approximately 83,000 tons of cargo in 2020.
Key Trading Partners: Primarily caters to cargo flights within Asia, dealing with countries like China, Japan, and Taiwan.
Strategic Importance: Gimpo Airport, located in the heart of Seoul, provides speedy access to the business district, expediting local distribution.
Notable Features: Known traditionally for passenger flights, Gimpo also has increasingly active cargo operations, especially for air freight needing quick access to Seoul.
For Your Business: If you’re shipping smaller volumes primarily within Asia and need quick distribution in Seoul, Gimpo's strategic location and growing cargo operations could offer a perfect solution.
Jeju International Airport
Cargo Volume: Handles approximately 30,000 tons of cargo annually.
Key Trading Partners: Primarily caters to regional destinations such as China, Japan, and domestic locations.
Strategic Importance: As the second-largest airport in Korea, Jeju plays a crucial role in catering to the domestic trade and some international cargo flights.
Notable Features: The airport's duty-free shopping sector introduces potential for value-added services and ecommerce fulfilment.
For Your Business: If you're involved in domestic trade or business within Asia focussed on small to medium sized cargo, Jeju’s growing capabilities matter for your distribution strategy.
Busan Gimhae International Airport
Cargo Volume: Approximate annual cargo volume of 134,000 tons.
Key Trading Partners: Frequent cargo flights to regional destinations, especially Japan and China.
Strategic Importance: Gimhae serves as the main international cargo airport for the Busan area, South Korea's industrial and trade hub.
Notable Features: Its proximity to Port of Busan facilitates multi-modal freight transport.
For Your Business: If your focus lies with multi-modal trade, especially within Asia, Busan Gimhae's location and link to the bustling port is particularly advantageous.
Daegu International Airport
Cargo Volume: Handles around 6,000 tons of cargo per year.
Key Trading Partners: Predominantly serves destinations within South Korea and key Asian trading partners.
Strategic Importance: As a critical regional airport, Daegu International is a hub for commercial and military flights in South Korea.
Notable Features: Its strategic location enables quick distribution around the manufacturing-rich Daegu region.
For Your Business: If your enterprise involves smaller cargo volumes and prioritizes rapid local distribution in and around Daegu, this airport should be on your radar.
How long does air freight take between Thailand and South Korea?
Typically, shipping goods between Thailand and South Korea by air freight can take between 1 to 3 days. However, this transit period can fluctuate depending on factors such as the origin and destination airports, the weight of your shipment, and the specific type of goods being transported. Ensuring efficient delivery requires a nuanced understanding of these factors. For accurate and tailored information specific to your shipment, consulting with an experienced freight forwarder, like DocShipper, is highly recommended.
How much does it cost to ship a parcel between Thailand and South Korea with air freight?
Shipping air freight between Thailand and South Korea broadly costs $1.50-$5.00 per kg, but exact rates can fluctuate widely. Factors such as proximity to departure and arrival airports, package dimensions, weight, and the nature of goods can all affect these costs. Unfortunately, universal pricing isn't possible due to these reasons. However, rest assured our expert team is committed to providing the most competitive rates tailored to your specific needs, as we quote prices case-by-case, ensuring that you only pay for what you need. Contact us today and receive a free customized quote within 24 hours.
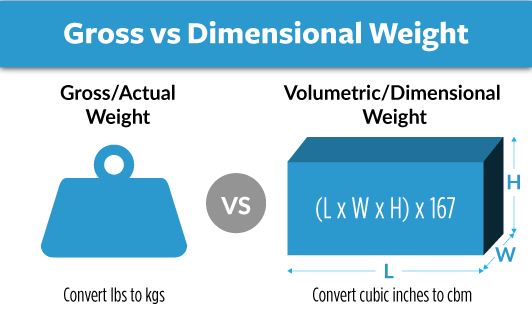
What is the difference between volumetric and gross weight?
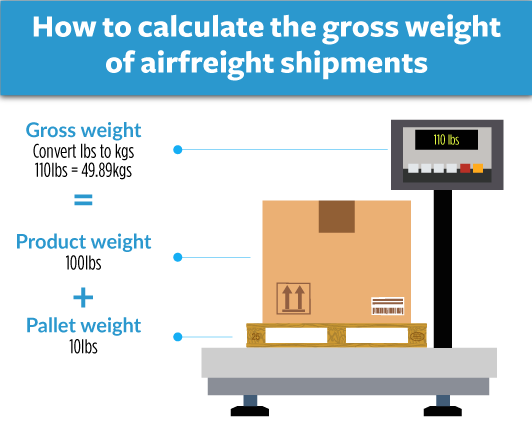
Gross weight refers to the actual physical weight of a shipment, including the goods and packaging. On the other hand, volumetric weight considers the amount of space the shipment occupies in the aircraft.
To calculate gross weight in air cargo, it's pretty straightforward - simply weigh the shipment as it is! For instance, if you have a shipment that weighs 30kg, that's your gross weight. Want this in lbs? That's approximately 66 lbs.
Volumetric weight is bit more involved. This is calculated by multiplying the dimensions of the package (length, width, height in cm) and then dividing by a standard divisor - typically, 6000 for air cargo and 5000 for express air freight services. For example, say you have a shipment in a box measuring 40 x 30 x 20 cm. For air cargo, the volumetric weight would be (40 x 30 x 20) / 6000 = 4kg, roughly 8.8 lbs.
Here's the twist though - air freight charges are typically based on whichever weight is greater: the gross weight or the volumetric weight. Therefore, even if your shipment is light, if it takes up a lot of space, you could end up paying more! So understanding these calculations can help you strategically pack and choose the options that make the most financial sense for your business.
Siam Shipping Tip: Consider Door to Door if:
- You value convenience and want a seamless shipping process, as door-to-door takes care of every step from pickup to delivery.
- You appreciate having a single point of contact, as door-to-door services typically provide a dedicated agent to handle all aspects of the shipment.
- You want less transitions for your cargo, reducing the risk of damage or loss, as door-to-door minimizes transitions between different modes of transport.
Door to door between Thailand and South Korea
Door to Door shipping is an international freight service that covers the entire logistics chain from pickup to delivery, all handled by one carrier. In the Thailand to South Korea route, it's a convenient and efficient choice, cutting through complex logistics and lengthy delays. What could that mean for your business? Countless benefits. So, ready to dive into door-to-door shipping? Let's unravel this!.
Overview – Door to Door
Shipping goods between Thailand and South Korea can feel like a complex, stressful task, right? But it doesn't have to be! With Door to Door services, logistics become hassle-free - your focus can be on running your business. Companies, like yours, cherish this approach for its simplicity and efficiency, making it the preferred choice among DocShipper clientele. Though slightly costlier, people find the ease of having goods picked up, professionally handled, and delivered to the doorstep outweighs the expense. Deciphering shipping regulations and unexpected fees? Leave that to us. Address your logistics challenges head-on with the reassurance of Door to Door shipping.
Why should I use a Door to Door service between Thailand and South Korea?
Are you tired of playing 'logistics tetris'? Look no further than Door-to-Door shipping services for transporting your goods between Thailand and South Korea. Here are five stress-busting reasons why you should consider this enticing service:
1. Hassle-free pick up and delivery: Remove the headache of logistics. Door-to-Door service handles your cargo right from the pickup point in Thailand to the final destination in South Korea. It's as easy as packing up, relaxing, and waiting for your goods to reach!
2. Timeliness: The clock's ticking and every second count for your urgent shipments. Door-to-Door service prides itself on punctuality, ensuring your freight arrives right on schedule.
3. Specialized care for intricate cargo: If you’re dealing with complex, delicate, or high-value goods, breathe easy. Specialists work to stipulate precise handling instructions and adopt protective measures to keep your cargo secure during transit.
4. The convenience of trucking services: Think of this as home delivery for your goods. Once your goods arrive in South Korea, the service continues right until your doorstep. No more separate trucking arrangements!
5. Stress relief: Unwind and let the experts handle the complex tapestry of customs clearance, hide 'n' seek with delivery trucks, and a thousand other tiny details.
With Door-to-Door service, transport your goods effortlessly between Thailand and South Korea. Want shipping without sweating? It's a Door-to-Door away!
DocShipper – Door to Door specialist between Thailand and South Korea
Simplify your Thailand-South Korea shipping with DocShipper's comprehensive door to door service. We manage everything - packing, transport, customs - regardless of the shipping method. Our specialized team ensures a hassle-free process. Plus, you’ll have a dedicated Account Executive to guide you. For a free estimate within 24 hours, reach out to us. Need advice? Our consultants are just a call away, ready to assist. Streamline your shipping process today with DocShipper.
Customs clearance in South Korea for goods imported from Thailand
Navigating the labyrinth of customs clearance, particularly for goods shipped from Thailand to South Korea, can be like wading through a marsh of unexpected fees and charges. This multifaceted process involves understanding customs duties, taxes, quotas, and licenses, any oversight of which could cause your goods to be stuck in limbo. If you don't want your goods to transforming into hefty costs, or worse, a logistical nightmare, our subsequent sections are just the compass you need. Don't worry, though! DocShipper is your reliable globe-trekking companion, paving your way in any corner of the world. Need a project budget estimate? Shoot us some details - origin, value, and HS Code of your goods. These keys will unlock your shipping project's cost estimate with us. Remember, in the world of international logistics, knowledge is your power!
How to calculate duties & taxes when importing from Thailand to South Korea?
Navigating the labyrinth of duties and taxes for imports can feel daunting, but with the right playbook, it can become doable and less intimidating. Understanding the typical components required to calculate customs duties is key to getting reliable estimates. You need to zero in on the country of origin - the place where your goods were actually manufactured or produced - the Harmonized System (HS) code, which is a standardised numerical method of classifying traded products, the customs value of your goods, the applicable tariff rate, and any other taxes or fees that may be levied on your products.
As the first maneuver in your estimation journey, you'll need to identify the actual birthplace of your goods. Are your goods genuinely Thai-made or just shipping from Thailand? This distinction is vital, as it can significantly impact the duties and taxes due. Once you have confirmed the country where the goods originated, you are well on your way to demystifying the import process.
Step 1 - Identify the Country of Origin
Nailing down the Country of Origin (COO), in this case, Thailand, is a rookie mistake to skip. Here's why:
1. Proof of Origin: Customs needs to know the origin of goods. It's part of their job to maintain national security and to enforce national laws.
2. Tariffs: South Korea has different tariffs arrangements with various countries. The Thailand-Korea FTA means lower or even no tariffs on certain goods.
3. Product Restrictions: Each nation possesses specific regulations. Knowing the COO helps anticipate possible restrictions and save you time and hassle.
4. Customs Procedures: The import process can vary based on COO. Maintain a smooth operation by understanding these differences.
5. Duty Relief: Benefiting from duty relief schemes like the ASEAN-Korea FTA requires clear COO documentation.
These trade agreements with Thailand can significantly cut your import costs. Stay alert to their specific conditions and benefits.
Remember, importing certain goods like agricultural products or live animals may face specific restrictions. Prioritize understanding these rules to ensure a hassle-free customs experience.
Pro tip: Always cross-check any ambiguities with customs officials or a trustworthy freight forwarder. This first step sets the groundwork for a successful import experience. Manage your risks, save money, and embrace a smoother process from the start.
Step 2 - Find the HS Code of your product
The Harmonized System (HS) Code, often simply called HS Code, is a universally accepted classification method for goods. Used by customs authorities around the globe, it aids in identifying products and applying the right taxes, duties, and regulatory controls during the import/export process.
To those new in the world of shipping, finding the HS code for a product may seem like a tricky task to maneuver. If you're facing a similar situation, the first and most straightforward approach is to ask your supplier directly. Since they're involved in importing and are familiar with related protocols, they will likely have access to this vital information.
If you can't retrieve the HS codes directly from your supplier, don't stress; there's another way. We are about to guide you through the steps of finding the HS code yourself.
First, head over to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule. This tool is designed to make your search for HS Codes easier.
Once you're there, type the name of the product into the search bar.
After hitting enter, focus your eyes on the Heading/Subheading column. This is where your HS code resides.
But take note: Accuracy is key when it comes to HS Codes. Choosing the wrong code isn't just a minor inconvenience - it can lead to shipment delays and potential fines. So ensure you're meticulous in your task and, if in doubt, always seek professional advice.
With these steps, finding an HS code should be a breeze, and you're on your way to making your shipping process smoother. If you're still confused, don't worry - here's an infographic showing you how to read an HS code.
Step 3 - Calculate the Customs Value
Understanding the customs value can seem like a puzzle, but it doesn't have to be. It's different from the actual product value because it includes more than just the item price. The customs value is actually the CIF value; which is the sum of the cost of your goods, your international shipping charges, and your insurance costs. So, if your goods cost $2000, your freight cost is $500, and insurance is $100, the total CIF or customs value is $2600. Knowing this amount is crucial as it directly affects the customs duties you'll pay for shipping your goods from Thailand to South Korea. It's all about the hidden costs within the international shipping process. With this knowledge in your arsenal, calculating customs duties is sure to be a smoother journey.
Step 4 - Figure out the applicable Import Tariff
An import tariff is essentially a tax imposed on goods imported from one country to another. In South Korea, the Harmonized System (HS) code is used to determine the tariff on each imported item.
Locating the appropriate tariff for your items in South Korea can be broken down into a few simple steps. First, identify the HS code for your product. For instance, let's say we're importing rubber shoes, which have an HS code of 6402.90.
Now, using the Korea Customs Service website, follow these steps:
1. Check 'Trade > Import/Export by HS Codes'
2. Insert the identified HS code in 'HS or Product description' option
3. Choose 'Thailand' in the 'Country(Region) of origin' dropdown section
4. Press 'Search'
The resulting screen will show you the applied duties and taxes on rubber shoes imported from Thailand.
Now, let's put this into practice with a real-world example. Assuming the CIF value (including costs, insurance, and freight) of the rubber shoes is $10,000, and the tariff rate shown for HS code 6402.90 is 13%, your total import duties paid would be $1,300. You will get this figure by calculating 13% of the CIF value ($10,000).
Remember, finding the right tariff and calculating duties requires a measure of precision. Use these insights as tools to make your process more efficient and less stressful.
Step 5 - Consider other Import Duties and Taxes
In addition to standard tariff rates, you might have to pay certain other import duties and taxes when shipping goods from Thailand to South Korea. For instance, excise duty may apply if you're importing tobacco, alcohol, or certain luxury items. Anti-dumping taxes could come into play if the product is suspected to be sold below its market value in its home country.
One key import cost you'll often face is the Value Added Tax (VAT). In South Korea, the VAT rate is usually around 10%, but it can vary. To estimate your VAT, you'd normally calculate it as a percentage of the customs value of your goods, plus any duties paid. It's important to consider these costs to avoid any surprises during the customs clearance process.
Remember, these are just examples, actual rates can differ. Make sure you consult with a customs expert or a reliable freight forwarder to get precise calculations and advice.
While maneuvering through customs might seem overwhelming, having a fundamental understanding of import duties and taxes could make the process smoother. Planning for these costs upfront can prevent unexpected expenses that can disrupt your business flow and budgeting. So don't overlook these extra charges when calculating your total import costs.
Step 6 - Calculate the Customs Duties
In this step, you'll understand how to calculate customs duties for your goods imported from Thailand to South Korea. The formula is typically as follows: Custom Duties = Customs Value x Duty Rate. However, other factors like VAT and anti-dumping taxes might intertwine.
Imagine importing goods with a customs value of $1000 and a duty rate of 5%. Your customs duty will be $50 (no VAT included). In a second scenario, if these goods are also subject to a 10% VAT, your total payable to customs will be $150 ($50 as customs duty + $100 as VAT).
Lastly, if you import goods with a customs value of $5000 and a duty rate of 10%, subject to a 15% VAT, 5% anti-dumping taxes, and $100 as Excise Duty, your total obligations to customs will be $1450 ($500 as customs duty, $750 as VAT, $250 as anti-dumping tax, and $100 as excise duty).
Complex, isn't it? This is where DocShipper steps in. We offer comprehensive customs clearance services worldwide, ensuring you never overpay. Reach out to us and we'll provide a free quote in less than 24 hours. Simplify your shipping experience with DocShipper. You can count on us for precision, compliance, and efficiency.
Does DocShipper charge customs fees?
Clearing up confusion, DocShipper, serving as your customs broker in Thailand and South Korea, does not impose your customs duties. Instead, it manages customs clearance fees on your behalf. Remember, these are two different things, like paying a courier fee versus a package’s VAT. Rest assured, DocShipper ensures transparency by providing official customs documentation. This way, you'll know you're paying only government-designated duties, nothing more.
Contact Details for Customs Authorities
Thailand Customs
Official name: Customs Department, Ministry of Finance, Thailand
Official website: http://www.customs.go.th/
South Korea Customs
Official name: Korea Customs Service
Official website: http://www.customs.go.kr/
Required documents for customs clearance
Facing a maze of paperwork? We'll demystify customs clearance by walking you through essential documents: the Bill of Lading, Packing List, Certificate of Origin, and Documents of conformity (CE standard). No more surprises or missing papers; clarity is just a few paragraphs away.
Bill of Lading
For traders negotiating the hubbub of Thailand-South Korea shipping, the Bill of Lading (BOL) is more than an official document—it's an assurance. It certifies the transfer of your cargo ownership securely, making it indispensable in ensuring your freight reaches its destination in Korea unscathed. Going telex? Electronic release streamlines logistics, saves processing time and makes your overall trading journey smoother. Don't forget the AWB for air cargo, same assurance, different altitude! Keep abreast with these procedures and watch your cross-border operations flourish. A little forethought here shaves off potential customs friction, making your shipping experience as palatable as a plate of kimchi!
Packing List
When shipping from Thailand to South Korea, your Packing List holds immense importance. Imagine it as your shipment's resume - it tells customs agents exactly what's inside your box, palette, or container. Accuracy here is key, you wouldn't want to misrepresent what's in your shipment. For instance, indicating 20 cartons of ceramics when you actually have 25 can result in delays during customs clearance, extra costs, or even legal issues, a situation no business wants to encounter. So, take your time while creating this document, regardless of whether you're sending your goods via air or sea. Double-check every item against its description, quantity, value, and weight. It may seem like a tedious task, but considering it from a cost, time-saving, and legal perspective, it's worth every minute. Remember, a well-prepared Packing List is your first step towards seamless freight forwarding between Thailand and South Korea.
Commercial Invoice
Perfecting your Commercial Invoice can save you headaches when shipping between Thailand and South Korea. This document verifies the value of goods and is pivotal for tax and duties calculation, so accuracy is crucial. It should include details like full addresses of the sender and recipient, a detailed description of your goods, country of origin, and Harmonized System codes. To avoid clearance issues, cross-check details with other shipping documents like the packing list or the Bill of Lading. Remember, discrepancies can lead to delays or higher taxes. For instance, if your Commercial Invoice lists 'machine parts' and your packing list mentions 'steel rods', customs might consider these as two different things. Keep it consistent and accurate to ensure smooth sailing.
Certificate of Origin
Navigating customs between Thailand and South Korea? Don't overlook the Certificate of Origin (COO). This crucial document states the country where your goods were produced, and it's your golden ticket to possibly benefiting from lower customs duty rates under the ASEAN-Korea Free Trade Agreement. As a Thailand-based business exporting electronic parts to South Korea, for instance, correctly issued COO can reduce or eliminate the usual 8% import tariff. But remember—the incorrect or incomplete COO can cause delays. So, spend some time ensuring your COO is up-to-date and error-free. It's a small effort for potentially significant savings and smooth shipping.
Get Started with Siam Shipping
Navigating customs clearance can be complex and time-consuming. Eliminate your worries with DocShipper's expertise! Our team will manage every step of the customs clearance process for you. Forget about the stress of documentation and compliance. Ready to switch to hassle-free and efficient shipping? Contact us today! We'll provide a free quote tailored to your needs within 24 hours. Start your stress-free shipping now!
Prohibited and Restricted items when importing into South Korea
Avoid costly shipment hold-ups or legal entanglements! Familiarizing yourself with South Korea's import regulations - knowing what's restricted or outright prohibited - is crucial. It can be a tricky terrain, but we're here to help you avoid common pitfalls.
Restricted Products
- Pharmaceuticals: You have to get the Pharmaceuticals Approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) you won't be able to import these products without it.
- Livestock products: The Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency (APQAIA) requires you to obtain a Livestock Products Import permit before you can take the product into South Korea.
- Pesticides: For these, the MFDS (Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) mandates a Pesticides Approval permit- so make sure you get it before importing any.
- Radio equipment: You need to secure a Radio Equipment Approval from the Korean Communications Commission (KCC).
- Medical devices: The Medical Device Approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) is a must-have if you're looking to import these.
Remember, these are only the high-level categories. South Korea has a complex list of restricted items and it might be helpful to check with a freight forwarder to ensure your specific product doesn't need extra permissions.
Prohibited products
- Narcotics and related utensils
- Counterfeit, altered, or imitation coins, paper money, banknotes
- Materials that infringe on or potentially infringe on copyrights and intellectual property rights
- Obscene or immoral materials including books, films, and other media
- Goods from communist states
- Certain animals and plants (including some fur products) without relevant certificates
- Soil and minerals unless authorized
- Radioactive materials
- Any kinds of meat coming from Hunter's game, meat from riding animals, and their products.
- Uncooked and unprocessed agricultural, forestry, and fishery products from countries or regions with reported outbreaks of harmful animal/plant diseases and pests
- All types of fresh fruits except those from Japan
- Animals or plants, or their products from the Democratic People's Republic of Korea.
Are there any trade agreements between Thailand and South Korea
Certainly, Thailand and South Korea enjoy a robust trading relationship thanks to the Korea-Thailand FTA. As a business, you'll appreciate significant tariff reductions and easier access to markets, enhancing your shipping efficiencies. Keep an eye out for ongoing talks for further collaborations and infrastructure projects, which may open new opportunities soon. Your shipping strategy may change significantly with the realization of such developments.
Thailand - South Korea trade and economic relationship
Thailand and South Korea share a robust economic partnership honed over decades. This relationship was officially cemented in 1989 with the signing of the "Agreement on Trade and Economic Cooperation." There has been a steady expansion across key sectors like electronics, automobiles, and agri-products since then. South Korea's direct investment in Thailand reached an impressive USD 1.2 billion in 2024, reflecting its substantial influence. Both countries closely traded goods worth USD 12 billion in the same year. A lion's share of this trade included commodities like integrated circuits, vehicle parts, and rubber. The intertwined economic relationship underscores a symbiotic bond that mutually enriches both nations in their journey towards growth and prosperity.
Your Next Step with Siam Shipping
Experience a worry-free shipment between Thailand and South Korea with DocShipper's expertise. Bid farewell to confusing protocols, complex customs, or outreach to multiple service providers - we handle it all. Rest assured, whether it’s air, sea, road, or rail, we’ve got your back. Ready to simplify your international shipping? Reach out to DocShipper now. Let's ship smarter, together.
Additional logistics services
Explore more than just shipping and customs! Enhance your supply chain with DocShipper's comprehensive logistics services, aimed at streamlining your journey from warehouse to final destination. We've got your back, every step of the way!
Warehousing and storage
Pinpointing trustworthy warehousing in unfamiliar territories can be taxing, especially with niche requirements like temperature control for product integrity. For instance, sensitive electronics or fine wines demand exact climate settings. Overcome these hurdles by exploring our comprehensive warehousing solutions. Cut through the hassle, and ensure optimal care for your goods. More info awaits on our dedicated page: Warehousing
Packaging and repackaging
When shipping goods from Thailand to South Korea, proper packaging is paramount to ensure your shipment arrives undamaged. With the right freight forwarder at your side, tasks like repackaging electronics, securing fragile ceramics, or wrapping textiles becomes less daunting. Our packaging and repackaging services are tailored to meet various product needs, providing peace of mind for your transnational shipping venture. More info on our dedicated page: Freight packaging
Cargo insurance
Shipping cargo always carries inherent risks. This is where cargo insurance outpaces fire insurance; it safeguards your consignments during transit, not just from fire, but also other mishaps like damage, theft, and loss at sea. For instance, a container of electronics gets damaged due to rough seas - cargo insurance makes sure you're covered. Mitigate those unpredictable risks with a touch of preparation. More info on our dedicated page: Cargo Insurance.
Supplier Management (Sourcing)
Struggling to find reliable suppliers for your Thailand-Korea shipping? Our team at DocShipper is committed to eradicating language barriers and simplifying supplier sourcing. Whether in Asia, East Europe, or beyond, we oversee your entire procurement process for a hassle-free experience. Imagine us as your professional procurement guide, leading you to trustworthy, quality suppliers. More details on how we can assist are on our Sourcing services page.
Personal effects shipping
Know the angst of moving personal stuff between Thailand and South Korea? Be it intricate artifacts or bulky furniture, your belongings are handled with utmost care and adaptability. Think of your delicate Thai porcelain making a safe journey to Busan. More info on our dedicated page: Shipping Personal Belongings.
Quality Control
Quality control is your secret weapon to ensure smooth shipping from Thailand to South Korea. It's the pivotal step to verify your goods are manufactured correctly and meet industry standards before they hit the road. Imagine sending automotive parts with undetected flaws - it's a recipe for returns and unhappy clients. With our quality inspections, we help avoid these setbacks, saving you time and stress. Want the inside track? More info on our dedicated page: Quality Inspection
Product compliance services
Staying on top of product regulations for international shipping can be tough. Our Product Compliance Services take this uncertainty out of your hands. We'll test your goods in our lab and assist in obtaining necessary certifications, ensuring they meet all destination regulations. No need for you to get buried in paperwork! Explore how we simplify this critical process on our Product compliance services page.
FAQ | Freight Forwarder in Thailand and South Korea
What is the necessary paperwork during shipping between Thailand and South Korea?
When shipping from Thailand to South Korea, key documents we'll need from you are the packing list and commercial invoice. If you're using sea freight, we handle the bill of lading, and for air freight, the air waybill is on us. Depending on what you're shipping, other documents - such as Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) or certification - might be necessary. Our aim at DocShipper is to streamline your shipping process, so we'll guide you through every step of the documentation process.
Do I need a customs broker while importing in South Korea?
Yes, engaging a customs broker while importing in South Korea is advised due to the intricate processes and mandatory documentation involved. At DocShipper, we act on your behalf, representing your cargo at customs for the majority of shipments. This simplifies your engagement with customs authorities, ensuring a more straightforward and efficient import process. Leveraging our expertise can help you navigate through the complexities of customs, ensuring a smoother shipping experience.
Can air freight be cheaper than sea freight between Thailand and South Korea?
While it's tricky to give a definitive answer since variables like route, weight, and volume play a part, air freight can act as a viable option for shipments less than 1.5 Cubic Meters or 300 kg. At DocShipper, we prioritize providing the most economical solution tailored to your shipment. Leveraging air freight for smaller, lighter cargo can often prove cost-effective. Your dedicated account executive will always ensure the best price-performance for your transport requirements. Remember, assessing the real cost goes beyond just the freight charges. It also considers the value of faster transit times and lower inventory costs that air freight can offer.
Do I need to pay insurance while importing my goods to South Korea?
As DocShipper, we advise you to consider getting an insurance policy while importing goods to South Korea, even though it isn't a legal obligation. The unpredictable nature of transport means that incidents which could damage, lose, or result in theft of your cargo can occur. Insurance provides a safety net in case of such mishaps and would cover the cost of your losses, safeguarding your business interests. Therefore, while it's not mandatory, it's a highly recommended strategy to protect your shipment.
What is the cheapest way to ship to South Korea from Thailand?
Based on the geographical proximity of Thailand and South Korea, the most economical shipping method we recommend is sea freight, particularly for heavy or bulky items. However, cost can vary depending on cargo size, type, and urgency. Therefore, we advise businesses to contact us for a tailored solution. Air freight can be considered for urgent, high-value, or perishable goods, despite it being costlier.
EXW, FOB, or CIF?
Choosing between EXW, FOB, or CIF depends on your relationship with your supplier. Remember, they might not have extensive logistics know-how, so it's beneficial to allow an agent like us, DocShipper, to manage the international shipping and destination process. Commonly, suppliers sell under EXW (from their factory door) or FOB (including all charges until the origin terminal). Regardless of the terms, we provide a comprehensive door-to-door service, simplifying your shipping needs.
Goods have arrived at my port in South Korea, how do I get them delivered to the final destination?
If we manage your cargo under CIF/CFR incoterms, you'll need a custom broker or freight forwarder to clear goods at the terminal and handle import charges and final delivery. However, we offer a DAP incoterms service, where we oversee the entire process for you. Please double-check this with your designated account executive to clarify the specifics.
Does your quotation include all cost?
Indeed, our quotations are designed to be completely transparent, including all costs, excluding only the duties and taxes at the destination. However, your dedicated account executive stands ready to provide an estimate for these. At DocShipper, we ensure no hidden fees surprise you in order to maintain clear, trustworthy partnerships.